For information on the latest version, please have a look at GL013302.
movel (Auto Mode)
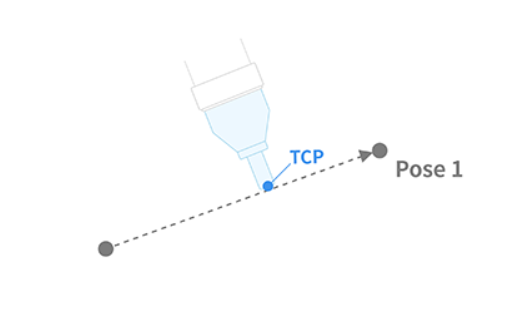
This is a function for moving the robot along a straight line to the target position (pos) within the task space in the robot controller.
Definition
DRFLEx.h within class CDRFLEx, public section (line 776)
// motion control: linear move
bool movel(float fTargetPos[NUM_TASK],
float fTargetVel[2],
float fTargetAcc[2],
float fTargetTime = 0.f,
MOVE_MODE eMoveMode = MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE,
MOVE_REFERENCE eMoveReference = MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE,
float fBlendingRadius = 0.f,
BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE eBlendingType = BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE_DUPLICATE,
DR_MV_APP eAppType = DR_MV_APP_NONE) {
return _movel(_rbtCtrl, fTargetPos, fTargetVel, fTargetAcc, fTargetTime,
eMoveMode, eMoveReference, fBlendingRadius, eBlendingType, eAppType);
};
Parameter
Parameter Name |
Data Type |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
fTargetPos |
float[6] |
Target TCP Position for six axes |
|
fTargetVel |
float[2] |
Linear Velocity, Angular Velocity |
|
fTargetAcc |
float[2] |
Linear Acceleration, Angular Acceleration |
|
fTargetTime |
float |
0.f |
Reach Time [sec] |
eMoveMode |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
|
eMoveReference |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
|
fBlendingRadius |
float |
0.f |
Radius for blending |
eBlendingType |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
|
eAppType |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
Note
If an argument is inputted to
fTargetVel(e.g.,{30, 0}), the input corresponds to the linear velocity of the motion, while the angular velocity is determined proportionally to the linear velocity.If an argument is inputted to
fTargetAcc(e.g.,{60, 0}), the input corresponds to the linear acceleration of the motion, while the angular acceleration is determined proportionally to the linear acceleration.If
fTargetTimeis specified, values are processed based onfTargetTime, ignoringfTargetVelandfTargetAcc.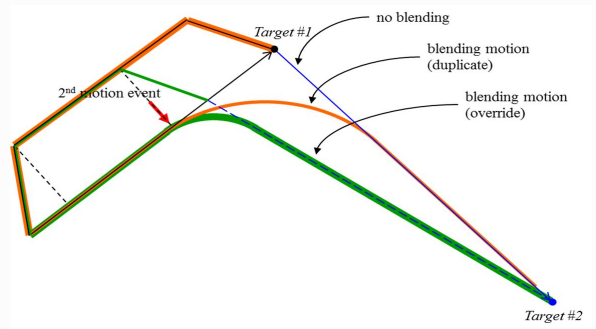
Caution
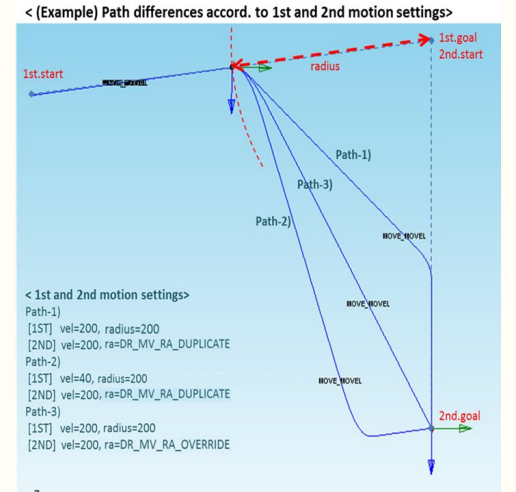
If the following motion is blended with the conditions of eBlendingType being
BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE_DUPLICATE and fBlendingRadius > 0, the preceding motion
can be terminated after the following motion is terminated first when the remaining
motion time, which is determined by the remaining distance, velocity, and
acceleration of the preceding motion, is greater than the motion time of the
following motion. Refer to the following image for more information.
Return
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Error |
1 |
Success |
Example
// CASE 1
float x1[6] = { 559, 434.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0 };
float tvel[2] = { 50, 50 };
float tacc[2] = { 100, 100 };
drfl.movel(x1, tvel, tacc);
// Moves to the x1 position with velocity 50(mm/sec) and acceleration 100(mm/sec2)
// CASE 2
float x1r[6] = { 559, 434.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0 };
float tTime = 5;
drfl.movel(x1r, 0, 0, tTime);
// Moves to the x1 position with a reach time of 5 sec.
// CASE 3
float x1t[6] = { 559, 434.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0 };
float tvel2 = 50;
float tacc2 = 100;
drfl.movel(x1t, tvel2, tacc2, 0, MOVE_MODE_RELATIVE, MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL);
// Moves the robot from the start position to the relative position of x1t in the tool coordinate.
float x1b[6] = { 559, 434.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0 };
float x2b[6] = { 559, 434.5, 251.5, 0, 180, 0 };
float tvelb[2] = { 50, 50 };
float taccb[2] = { 100, 100 };
float blending_radius = 100;
drfl.movel(x1b, tvelb, taccb, 0, MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE, MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE, blending_radius);
This example demonstrates linear TCP motion using velocity/acceleration, time-based execution, a relative tool-frame move, and a blended linear segment using a 100 mm radius to smoothly connect to the next path.