For information on the latest version, please have a look at GL013302.
movejx (Auto Mode)
This function moves the robot to a target TCP position (posx) defined in the task space while performing the motion in joint space. Although it accepts a Cartesian target like movel, the internal trajectory is executed through joint interpolation rather than linear path planning.
The target pose can be reached via one of eight robot configurations (solution spaces),
and the user must specify the desired configuration index (0–7).
If 255 is entered, the robot automatically selects the configuration closest
to the current joint posture (based on the smallest L2 norm of joint axes 2–5).
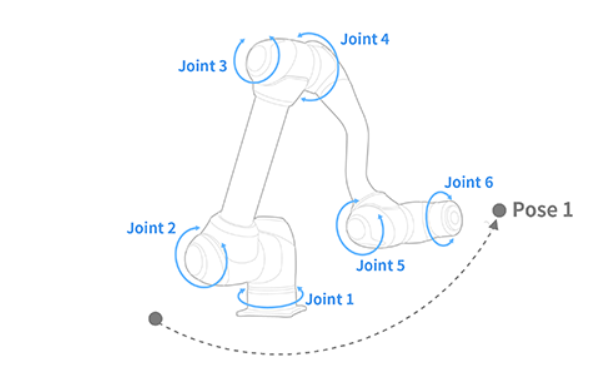
Definition
DRFLEx.h within class CDRFLEx, public section (line 790)
bool movejx(float fTargetPos[NUM_JOINT],
unsigned char iSolutionSpace,
float fTargetVel,
float fTargetAcc,
float fTargetTime = 0.f,
MOVE_MODE eMoveMode = MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE,
MOVE_REFERENCE eMoveReference = MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE,
float fBlendingRadius = 0.f,
BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE eBlendingType = BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE_DUPLICATE) {
return _movejx(_rbtCtrl, fTargetPos, iSolutionSpace, fTargetVel, fTargetAcc,
fTargetTime, eMoveMode, eMoveReference, fBlendingRadius, eBlendingType);
};
Parameter
Parameter Name |
Data Type |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
fTargetPos |
float[6] |
Target TCP position (X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz) |
|
iSolutionSpace |
unsigned char |
Joint configuration index (0–7 or 255 for auto selection) |
|
fTargetVel |
float |
Velocity [mm/s or deg/s] |
|
fTargetAcc |
float |
Acceleration [mm/s² or deg/s²] |
|
fTargetTime |
float |
0.f |
Reach time [sec] (overrides velocity and acceleration) |
eMoveMode |
|
Defines absolute or relative motion mode |
|
eMoveReference |
|
Coordinate reference system (BASE or TOOL) |
|
fBlendingRadius |
float |
0.f |
Radius for blending consecutive motions [mm] |
eBlendingType |
|
Blending type option for transition smoothing |
Note
When
fTargetTimeis specified, the system ignoresfTargetVelandfTargetAccand moves according to the specified duration.Using blending after relative motion (
MOVE_MODE_RELATIVE) can cause errors. Blending should be used only with absolute mode.Refer to movej and movel for more details on blending methods according to
fBlendingRadiusandfBlendingType.
Robot configuration (solution space)
Solution Space |
Binary |
Shoulder |
Elbow |
Wrist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
000 |
Lefty |
Below |
No Flip |
1 |
001 |
Lefty |
Below |
Flip |
2 |
010 |
Lefty |
Above |
No Flip |
3 |
011 |
Lefty |
Above |
Flip |
4 |
100 |
Righty |
Below |
No Flip |
5 |
101 |
Righty |
Below |
Flip |
6 |
110 |
Righty |
Above |
No Flip |
7 |
111 |
Righty |
Above |
Flip |
255 |
Auto |
- |
- |
Automatically selects configuration closest to current posture (minimizes L2 norm of joint axes 2–5) |
Return
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Error |
1 |
Success |
Example
// CASE 1 — Velocity/acceleration-based joint-space move
float x1[6] = {559, 34.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0};
unsigned char sol = 2;
float jvel = 10;
float jacc = 20;
drfl.movejx(x1, sol, jvel, jacc);
// Moves to the target pose corresponding to x1
// using velocity 10 deg/s and acceleration 20 deg/s².
// CASE 2 — Time-based motion
float x2[6] = {559, 34.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0};
drfl.movejx(x2, sol, 0, 0, 5);
// Moves to the target joint configuration in 5 seconds.
// CASE 3 — Motion blending with previous move
float x3[6] = {559, 34.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0};
float x4[6] = {559, 434.5, 651.5, 0, 180, 0};
float blend_radius = 50;
drfl.movejx(x3, sol, jvel, jacc, 0, MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE, MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE, blend_radius);
drfl.movejx(x4, sol, jvel, jacc, 0, MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE, MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE, 0, BLENDING_SPEED_TYPE_DUPLICATE);
// Executes blended joint-space motion between x3 and x4
// maintaining smooth transition within 50 mm radius.
This function is mainly used for high-speed, smooth joint-space transitions that maintain stable configuration tracking while ensuring flexible blending control.