For information on the latest version, please have a look at GL013302.
move_periodic (Auto Mode)
This function performs cyclic motion for each axis based on the sine function. The motion is executed as a relative periodic trajectory from the current position, where the amplitude, period, acceleration time, and repetition count determine the waveform. Each axis (X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz) can be independently configured to generate synchronized sinusoidal motion according to the reference frame.
Definition
DRFLEx.h within class CDRFLEx, public section (line 808)
bool move_periodic(float fAmplitude[NUM_TASK],
float fPeriodic[NUM_TASK],
float fAccelTime,
unsigned int nRepeat,
MOVE_REFERENCE eMoveReference = MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL) {
return _move_periodic(_rbtCtrl, fAmplitude, fPeriodic, fAccelTime, nRepeat, eMoveReference);
};
Parameter
Parameter Name |
Data Type |
Range / Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
fAmplitude |
float[6] |
≥ 0 |
Amplitude of motion between -fAmplitude and +fAmplitude [mm] or [deg] (axes: x, y, z, Rx, Ry, Rz) |
fPeriodic |
float[6] |
≥ 0 |
Period time for one motion cycle [sec] |
fAccelTime |
float |
≥ 0 |
Acceleration / deceleration time [sec] |
nRepeat |
unsigned char |
> 0 |
Number of periodic repetitions |
eMoveReference |
MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL |
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
Note
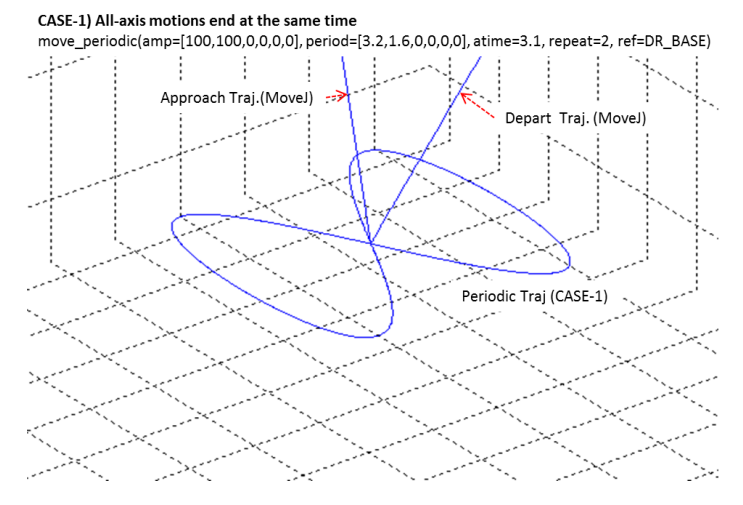
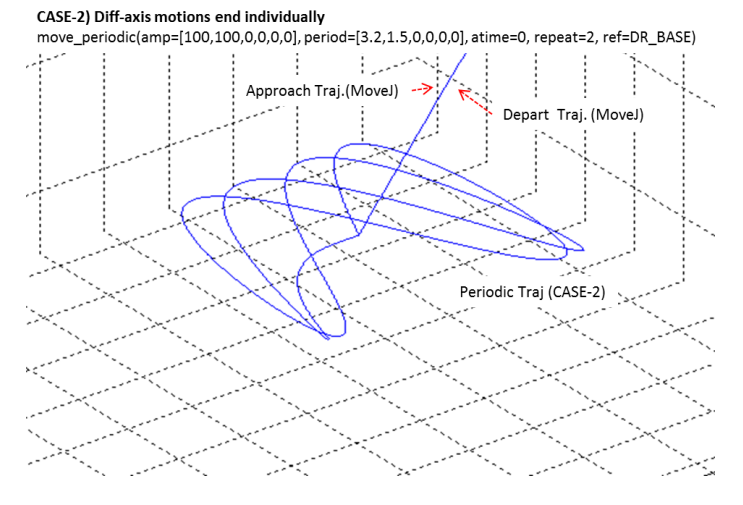
fAmplitudedefines the displacement range for each axis. Set unused axes to 0.fPeriodicdefines the time to complete one cycle per axis. Each element corresponds to X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, and Rz.fAccelTimespecifies the acceleration and deceleration interval at both ends of motion. The maximum allowed value is up to ¼ of the smallest period time.nRepeatdetermines how many cycles are repeated. If one axis has a larger period, that axis becomes the reference for total duration.If the motion ends normally, shorter-period axes terminate earlier, and the robot returns to the initial position when all axes complete their cycles.
eMoveReferencedetermines whether periodic motion is performed in the BASE or TOOL coordinate system.The maximum achievable velocity can be estimated by:
velocity = (Amplitude × 2 × π × 3.14) / Period
Example: amplitude = 10 mm, period = 1 s → max velocity ≈ 62.83 mm/s
Online blending with other motions is not supported.
Return
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Error |
1 |
Success |
Example
// CASE 1 — TOOL reference periodic motion
float fAmplitude[NUM_TASK] = {10, 0, 0, 0, 30, 0};
float fPeriod[NUM_TASK] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1};
drfl.move_periodic(fAmplitude, fPeriod, 0.2, 5, MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL);
// Repeats x-axis (10 mm amp, 1 sec period) and Ry rotation (30° amp) motion 5 times.
// CASE 2 — BASE reference periodic motion
float amp2[NUM_TASK] = {10, 20, 0, 0, 0, 5};
float per2[NUM_TASK] = {1, 0, 1.5, 0, 0, 0};
drfl.move_periodic(amp2, per2, 0.5, 3, MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE);
// Repeats x-axis (10 mm, 1 sec) and z-axis (20 mm, 1.5 sec) motion 3 times.
// Axes with period = 0 (like y, rx, ry) remain fixed.
// Total duration ≈ 5.5 s; x-axis completes ~4.5 cycles.
This command generates smooth cyclic trajectories for each specified axis and is commonly used for vibration testing, oscillation calibration, or dynamic tool testing.