For information on the latest version, please have a look at GL013302.
moveb (Auto Mode)
This is a function for moving the robot at constant velocity by blending the robot with the blending radius set in the path information after receiving path information consisting of one or more lines or arcs.
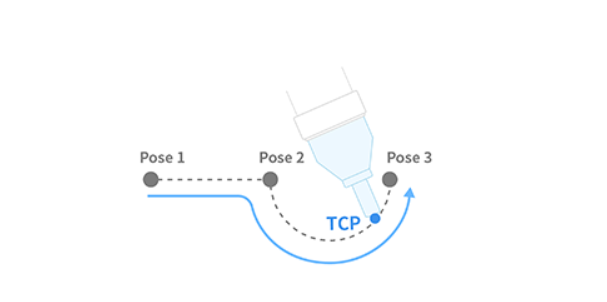
Definition
DRFLEx.h within class CDRFLEx, public section (line 787)
// motion control: blending move
bool moveb(MOVE_POSB tTargetPos[MAX_MOVEB_POINT],
unsigned char nPosCount,
float fTargetVel[2],
float fTargetAcc[2],
float fTargetTime = 0.f,
MOVE_MODE eMoveMode = MOVE_MODE_ABSOLUTE,
MOVE_REFERENCE eMoveReference = MOVE_REFERENCE_BASE,
DR_MV_APP eAppType = DR_MV_APP_NONE) {
return _moveb(_rbtCtrl, tTargetPos, nPosCount, fTargetVel, fTargetAcc,
fTargetTime, eMoveMode, eMoveReference, eAppType);
};
Parameter
Parameter Name |
Data Type |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
tTargetPos |
MOVE_POSB [MAX_MOVEB_POINT] |
Maximum 25 path information |
|
nPosCount |
unsigned char |
Number of valid paths |
|
fTargetVel |
float[2] |
Linear Velocity, Angular Velocity |
|
fTargetAcc |
float[2] |
Linear Acceleration, Angular Acceleration |
|
fTargetTime |
float |
0.f |
Reach Time [sec] |
eMoveMode |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
|
eMoveReference |
|
Refer to the Definition of Enumeration Type |
Note
If an argument is inputted to
fTargetVel(e.g.,{30, 0}), the input corresponds to the linear velocity of the motion, while the angular velocity is determined proportionally to the linear velocity.If an argument is inputted to
fTargetAcc(e.g.,{60, 0}), the input corresponds to the linear acceleration of the motion, while the angular acceleration is determined proportionally to the linear acceleration.If
fTargetTimeis specified, values are processed based onfTargetTime, ignoringfTargetVelandfTargetAcc.When
eMoveModeisMOVE_MODE_RELATIVE, each pos on the posb list is defined as a relative coordinate for the preceding pos.
Caution
A user input error is generated if the blending radius in
tTargetPosis 0.A user input error is generated due to the duplicated input of Line if contiguous Line–Line segments have the same direction.
If the blending condition causes a rapid change in direction, a user input error is generated to prevent sudden acceleration.
This function does not support online blending of previous and subsequent motions.
Return
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Error |
1 |
Success |
Example
MOVE_POSB xb[4];
memset(xb, 0x00, sizeof(xb));
int seqNum = 4;
float tvel[2] = { 50, 50 };
float tacc[2] = { 100, 100 };
xb[0]._blendType = 0; // line
xb[0]._fBlendRad = 50;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[0] = 559;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[1] = 234.5;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[2] = 651.5;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[3] = 0;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[4] = 180;
xb[0]._fTargetPos[5] = 0;
xb[1]._blendType = 1; // circle
xb[1]._fBlendRad = 50;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[0] = 559;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[1] = 234.5;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[2] = 451.5;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[3] = 0;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[4] = 180;
xb[1]._fTargetPos[5] = 0;
xb[2]._blendType = 0; // line
xb[2]._fBlendRad = 50;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[0] = 559;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[1] = 434.5;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[2] = 451.5;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[3] = 0;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[4] = 180;
xb[2]._fTargetPos[5] = 0;
xb[3]._blendType = 0; // line
xb[3]._fBlendRad = 50;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[0] = 559;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[1] = 234.5;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[2] = 251.5;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[3] = 0;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[4] = 180;
xb[3]._fTargetPos[5] = 0;
// Moves the robot from the current position through a trajectory consisting of LINE–CIRCLE–LINE–LINE,
// maintaining velocity 50 (mm/sec, deg/sec) and acceleration 100 (mm/sec2, deg/sec2).
// Blending to the next segment begins when the distance of 50 mm from the end point of each segment is reached.
drfl.moveb(xb, seqNum, tvel, tacc);
This example executes a blended path of line and circular segments at constant speed/acceleration, using a 50 mm blend radius to smoothly connect each segment.