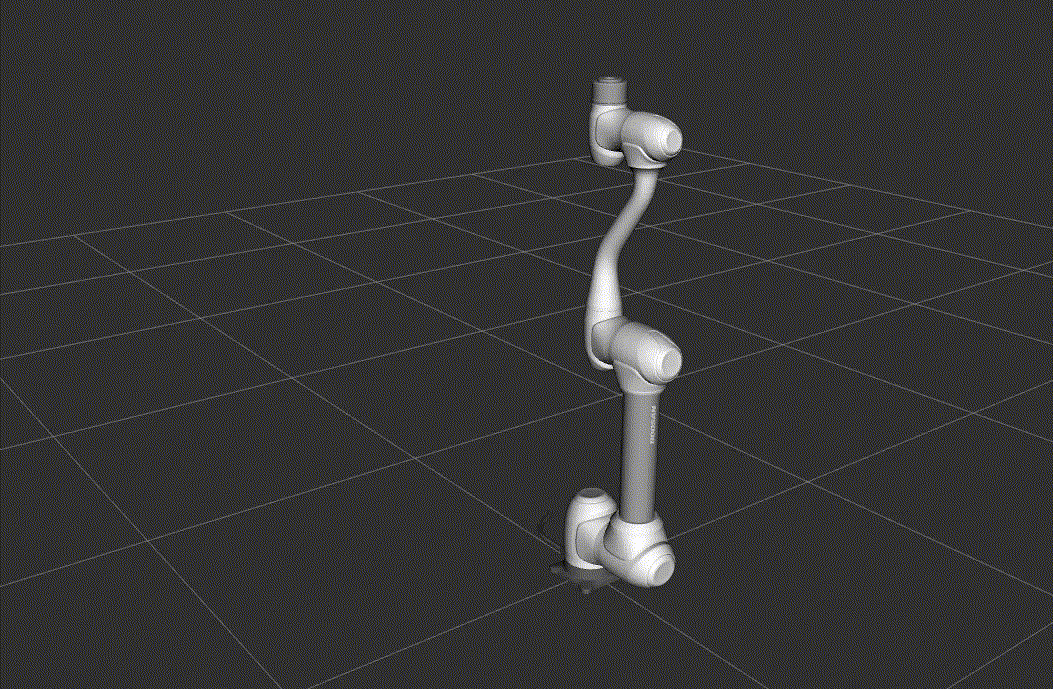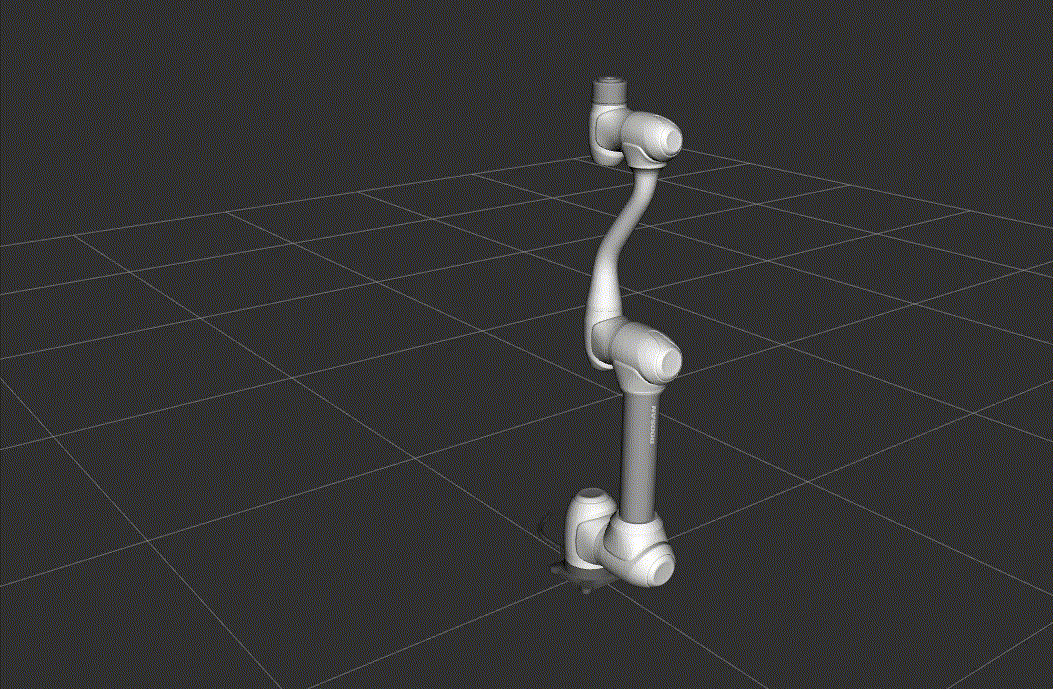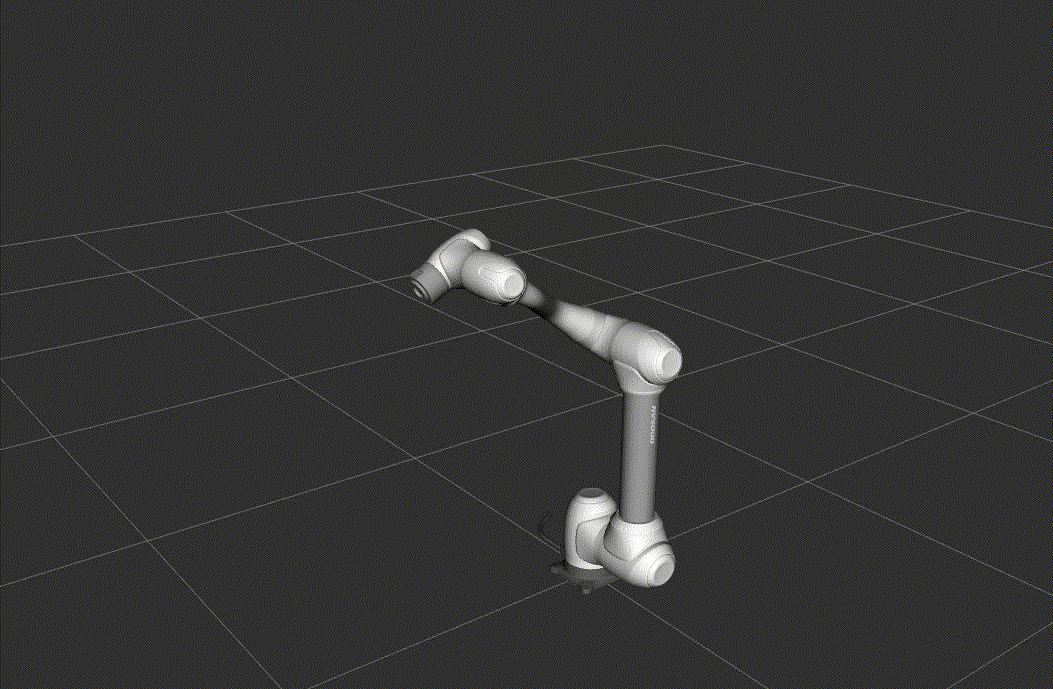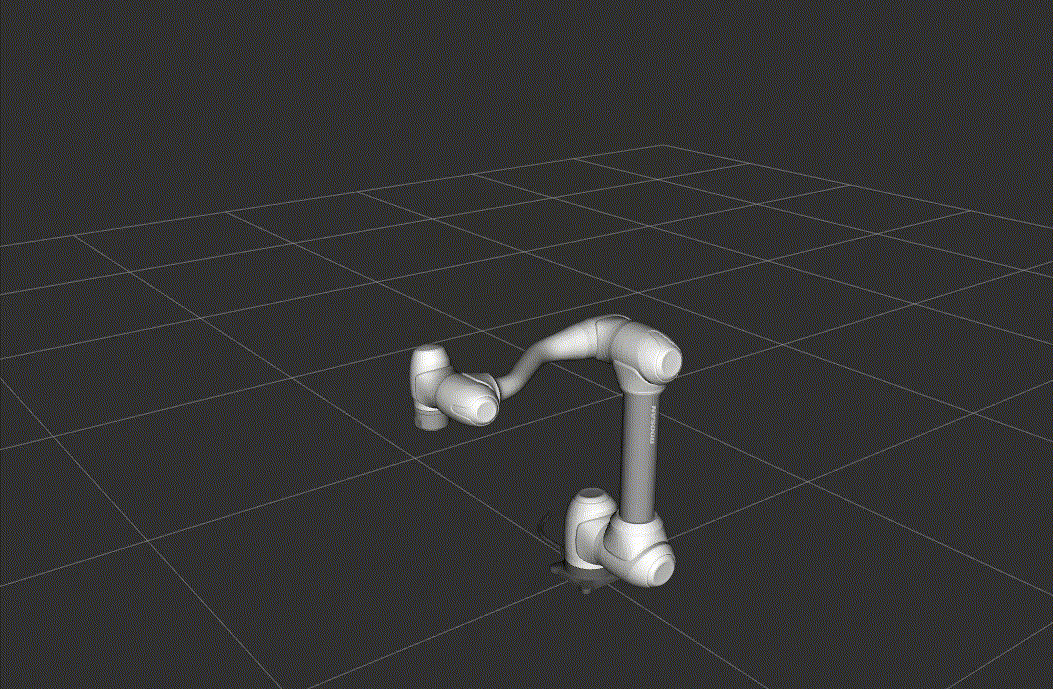RViz2 Launch
This launch file starts Rviz2 for visualizing the robot model and its state.
Command
ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_rviz.launch.py [arguments]
Arguments
mode: Robot operation mode. Choose between:real: Connect to physical Doosan robot.virtual: Run in simulator/emulator mode.
model: Robot model name (e.g.,m1013,a0509, etc.)host: IP address of the robot controller (real mode) or emulator (virtual mode)
Examples
Launch
To ensure proper launch and connection, the mode and host arguments should be configured accordingly.
Using a real robot:
Establish an Ethernet connection with your PC.
Verify the IP address on the robot controller and ensure it matches the connection settings.
ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_rviz.launch.py mode:=real host:=192.168.137.100 model:=m1013
Using a virtual robot:
Virtual IP address will always be
127.0.0.1.ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_rviz.launch.py mode:=virtual host:=127.0.0.1 model:=m1013
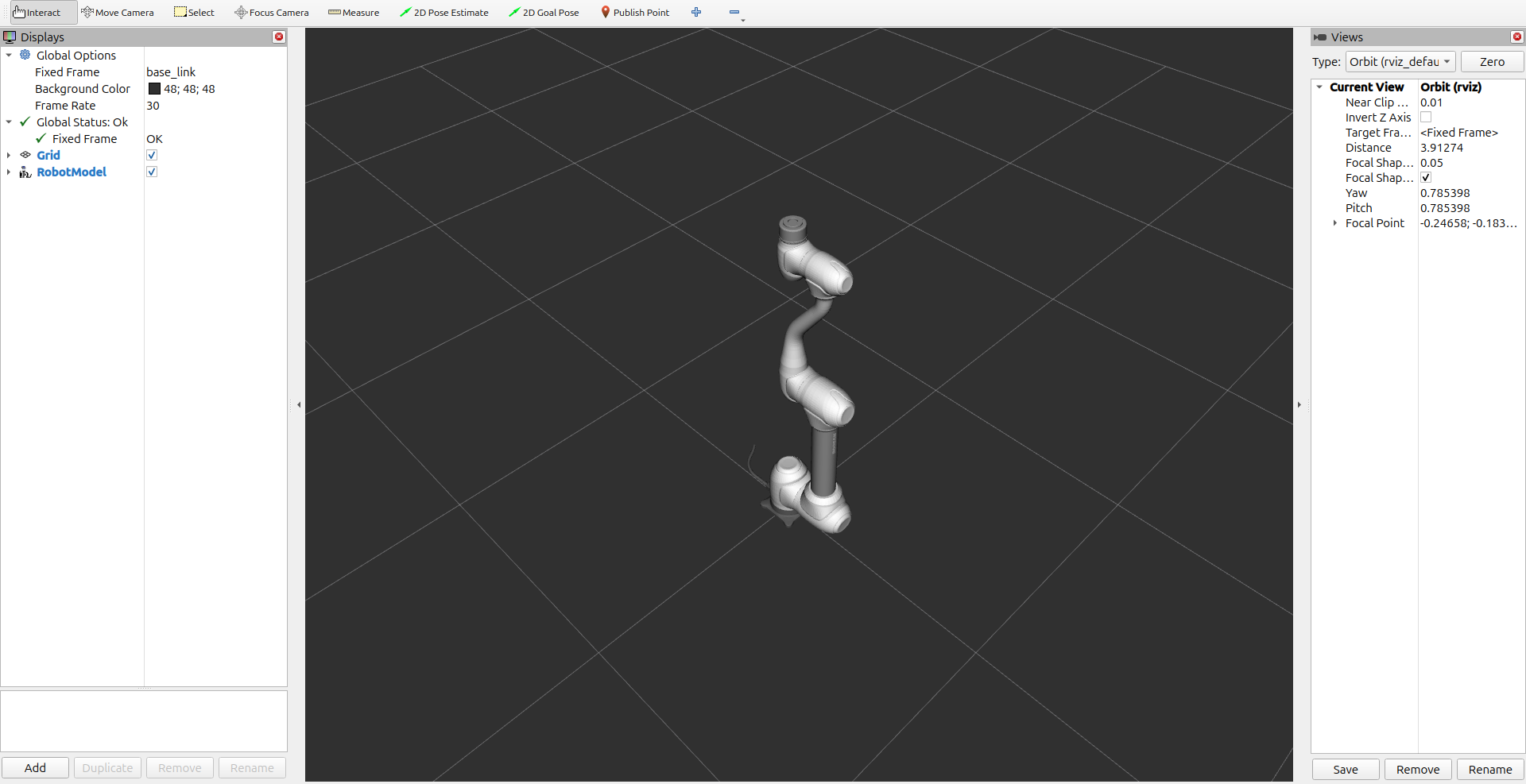
Launch with different model and configurations:

ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_rviz.launch.py mode:=virtual host:=127.0.0.1 model:=m0609

ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_rviz.launch.py mode:=virtual host:=127.0.0.1 model:=h2017 color:=blue
Note
You can check the available robot models in the
dsr_description2package.
Example move
Once RViz2 is running, you can test the setup by executing a simple motion script.
Open a new terminal and run the following command:
ros2 run dsr_example single_robot_simple
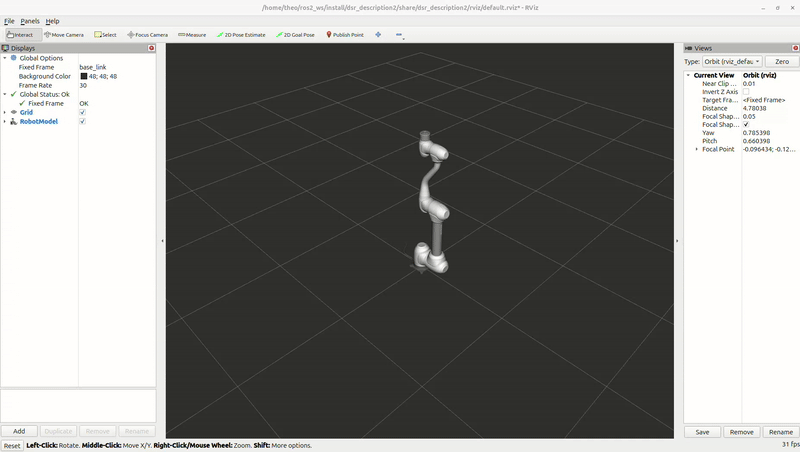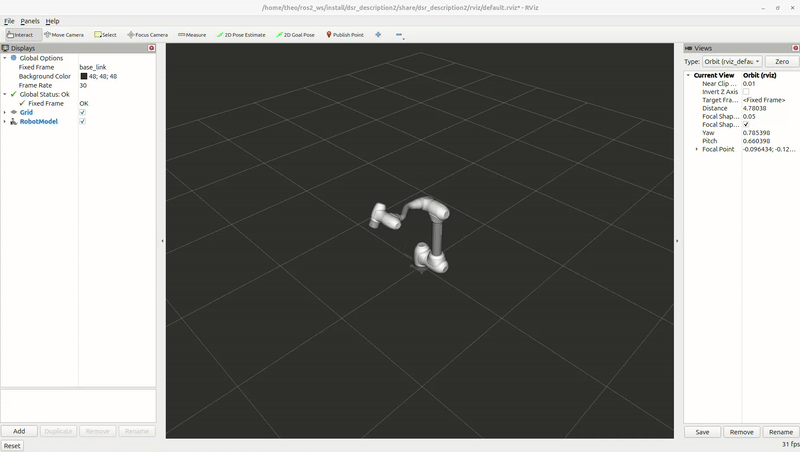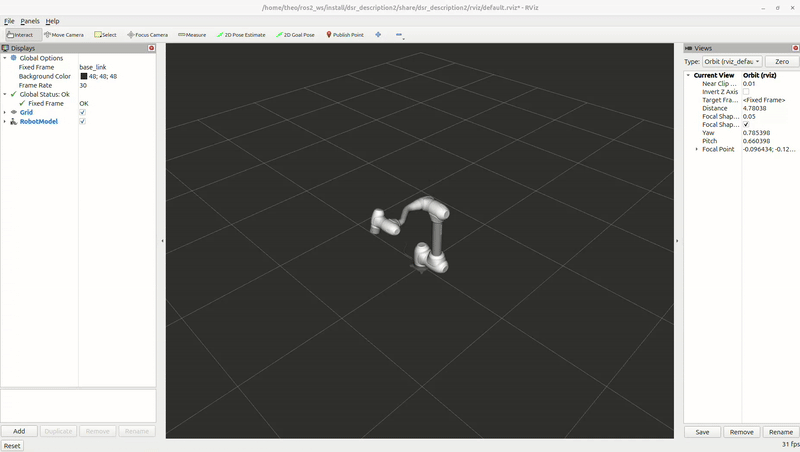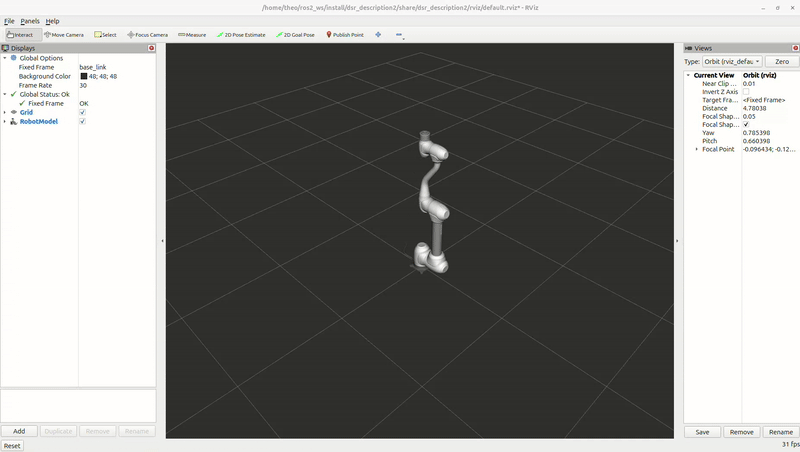
Note
Example scripts are available in dsr_example2 package.
Or you can directly move the robot by calling a service or topic :
ros2 service call /dsr01/motion/move_joint dsr_msgs2/srv/MoveJoint "{
pos: [0.0, 0.0, 90.0, 0.0, 90.0, 0.0],
vel: 100.0,
acc: 100.0,
time: 2.0,
mode: 0,
radius: 0.0,
blend_type: 0,
sync_type: 0
}"