Operation Modes
This section describes the operation modes available for the Doosan robot system.
Virtual Mode
Use virtual mode when operating without a physical robot. (Docker is required)
If you omit the mode argument, it defaults to virtual.
ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_gazebo.launch.py mode:=virtual
When launched in virtual mode, the emulator containing a virtual robot and controller (DRCF: Doosan Robot Controller Framework) will automatically start and stop during the launch lifecycle.
Note
Emulator location:
dsr_common2/bin/One emulator instance will be launched for each robot.
The system automatically assigns different ports for multiple robots.
To check if the emulator is running correctly, you can use the following command after launch:
docker ps # If emulator runs in Docker container
The output should look something like this:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
28c08ed25f1b doosanrobot/dsr_emulator:3.0.1 "/bin/bash /start_se…" 21 seconds ago Up 20 seconds 1122/tcp, 3601/tcp, 0.0.0.0:12345->12345/tcp, [::]:12345->12345/tcp dsr01_emulator
Real Mode
Use real mode when controlling an actual robot.
In real mode, the system communicates with the physical robot controller over TCP/IP.
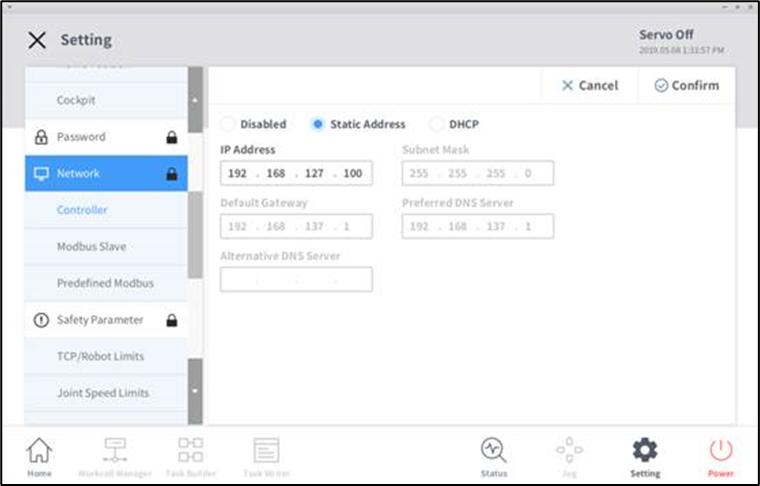
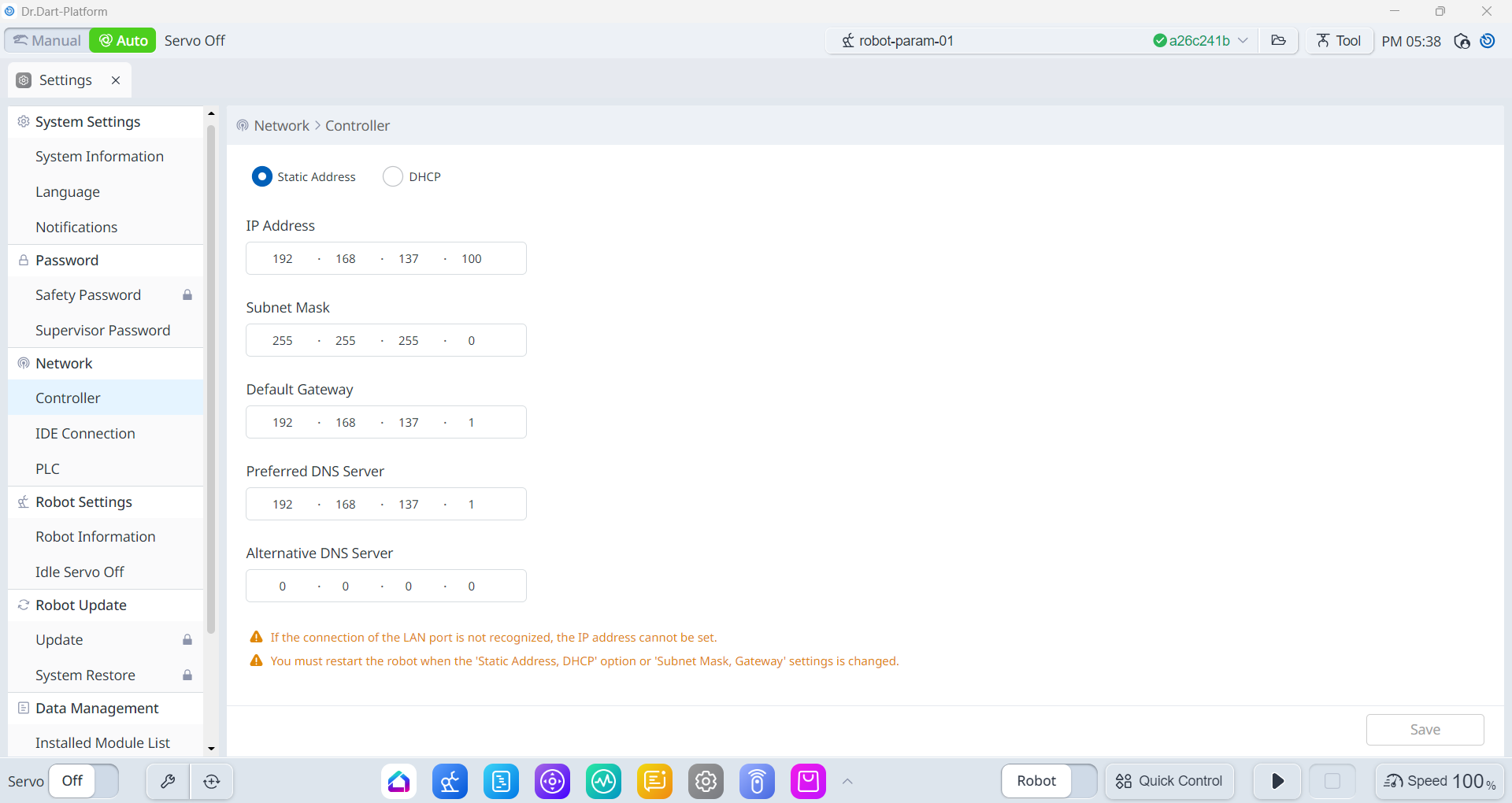
Default IP:
192.168.137.100Default Port:
12345
Pass the following arguments to launch in real mode:
ros2 launch dsr_bringup2 dsr_bringup2_gazebo.launch.py mode:=real host:=192.168.137.100 port:=12345
Note
Make sure your PC is connected to the same subnet as the robot controller.
(e.g., PC IP: 192.168.137.X)
Connect with the Real Robot Controller
Turn on the robot and check the Teach Pendant screen.
The images on the left is for the legacy version. The images on the right is for v3.0 or higher.
Navigate to
Settings → Networkand confirm the controller IP.
Use this IP address as the
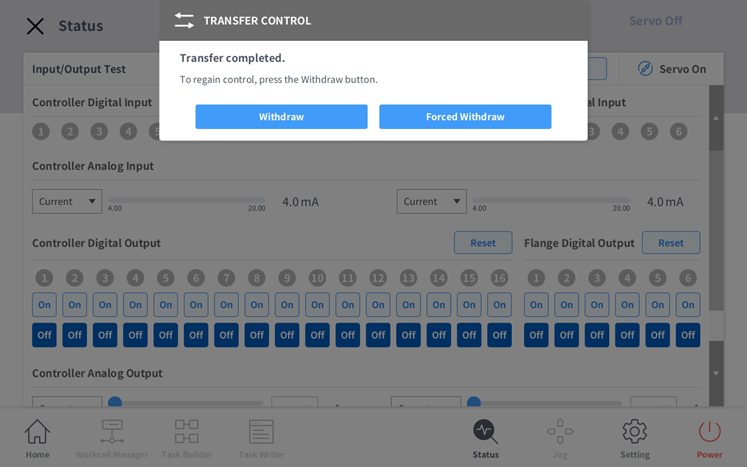
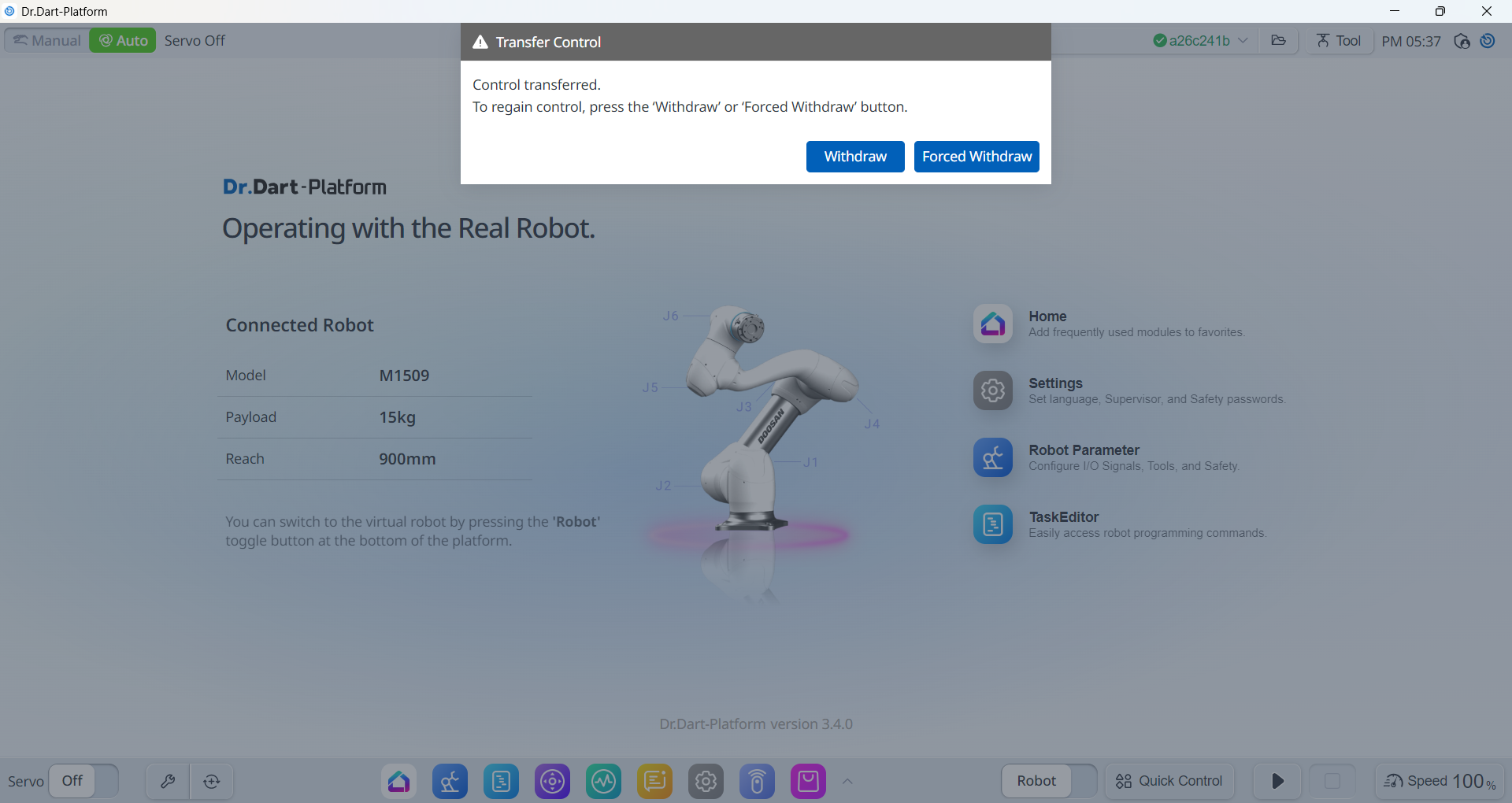
hostargument in your launch command.If ROS 2 control node is running successfully, the control will transfer from the TP to ROS 2.
A pop-up will appear on the TP confirming the transfer is complete.